Renal diseases, also known as kidney diseases, encompass a broad range of conditions that affect the proper functioning of the kidneys. These vital organs play a crucial role in filtering waste products from the blood and regulating fluid balance in the body. Understanding renal health is essential as these diseases can significantly impact overall well-being.
Common Types of Renal Diseases
Chronic kidney disease (CKD): A progressive condition that results in the gradual loss of kidney function over time.
Acute kidney injury (AKI): A sudden and temporary decline in kidney function, often caused by factors such as dehydration or medication toxicity.
Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the glomeruli, the tiny structures in the kidneys responsible for filtering blood.
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD): A genetic disorder characterized by the growth of cysts in the kidneys, which can lead to kidney failure if left untreated.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Early detection of renal diseases is crucial for effective management. Symptoms may include fatigue, swelling, changes in urine output, and high blood pressure. Diagnostic tests such as blood tests, urine tests, and imaging studies can help identify underlying kidney problems.
Treatment Options
Treatment for renal diseases varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. Medications may be prescribed to control symptoms and slow disease progression. In advanced cases, dialysis or kidney transplant may be necessary to replace lost kidney function.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing renal diseases. Following a kidney-friendly diet, engaging in regular exercise, and practicing stress management techniques can help improve overall kidney health.
Managing Complications
Renal diseases can lead to various complications, including hypertension, anemia, and bone problems. Managing these issues through medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle adjustments is essential for maintaining quality of life.
Support Systems
Living with a renal disease can be challenging, but having a strong support system in place can make a difference. Family, friends, support groups, and counseling services can provide emotional support and practical assistance to patients and their caregivers.
Navigating Life with Renal Diseases
Coping with a chronic illness requires resilience and adaptability. Setting realistic goals, maintaining a positive attitude, and seeking help when needed are crucial steps in navigating life with a renal disease.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
After undergoing treatment, patients may require ongoing care and rehabilitation to regain strength and function. Rehabilitation programs tailored to individual needs can help optimize recovery and prevent complications.
Prevention Strategies For Renal Diseases
While some renal diseases are genetic or unavoidable, adopting preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing kidney problems. This includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and avoiding exposure to harmful substances.
Understanding the Emotional Impact
Living with a chronic illness can take a toll on mental health. It’s essential for patients to acknowledge and address their emotions, whether it’s fear, anxiety, or depression. Seeking support from loved ones and mental health professionals can help manage these feelings effectively.
Financial Considerations
The cost of treating renal diseases can be significant, and financial concerns may add to the stress of managing the condition. Patients should explore insurance coverage options, financial assistance programs, and other resources to alleviate financial burden.
Resources for Patients and Caregivers
Numerous resources are available to help patients and their caregivers navigate the challenges of living with a renal disease. Reliable websites, educational materials, and support hotlines can provide valuable information and assistance.
Research and Innovation
Ongoing research and innovation in the field of renal care offer hope for improved treatment options and better outcomes for patients. Participating in clinical trials and staying informed about advancements in the field can provide opportunities for access to cutting-edge therapies.
Research and Innovation in Renal Care
Continued advancements in medical research and technology offer promising avenues for the treatment and management of renal diseases. Researchers are continually exploring new therapies and interventions aimed at improving outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Clinical Trials: Advancing Treatment Options
Clinical trials play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of renal diseases and evaluating the effectiveness of novel treatments. By participating in these studies, patients can contribute to the development of groundbreaking therapies and gain access to cutting-edge treatments that may not yet be available to the general public.
Precision Medicine: Tailoring Treatment Approaches
One area of innovation in renal care is the development of precision medicine approaches tailored to individual patients’ genetic makeup and disease characteristics. By analyzing genetic markers and other biological factors, clinicians can better predict disease progression and customize treatment plans to optimize outcomes.
Regenerative Medicine: Restoring Kidney Function
Another area of focus is regenerative medicine, which holds promise for repairing damaged kidney tissue and restoring lost function. Stem cell therapies, tissue engineering techniques, and organ regeneration strategies are being investigated as potential avenues for treating renal diseases and reducing the need for dialysis or transplantation.
Digital Health Technologies: Transforming Care Delivery For Renal Diseases
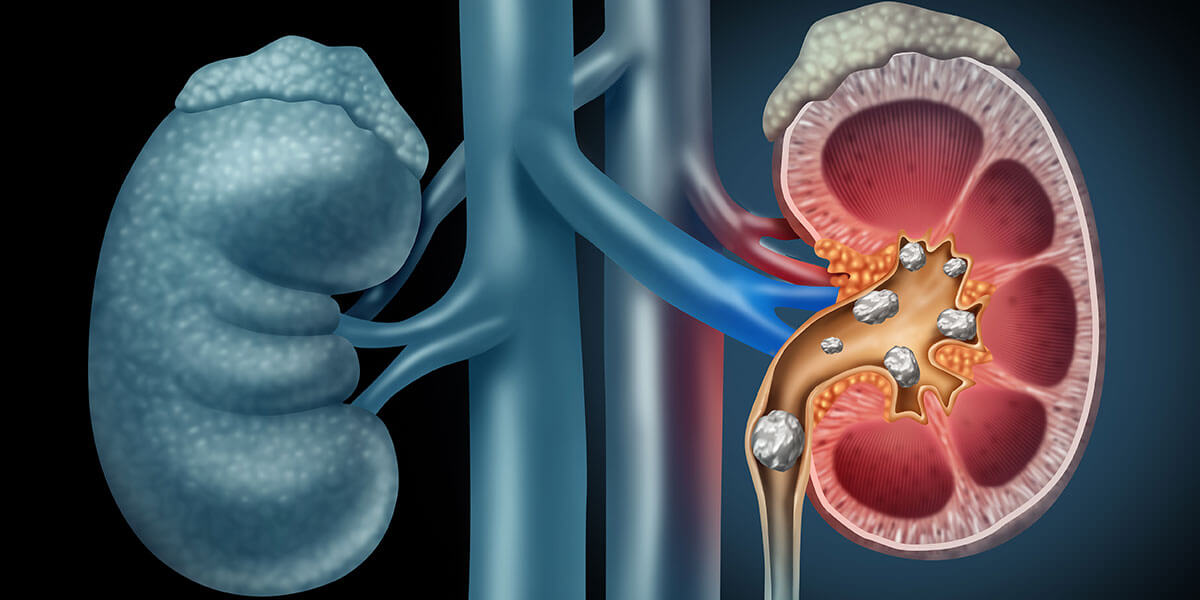
In addition to medical interventions, digital health technologies are revolutionizing the way renal care is delivered and managed. Telemedicine platforms, remote monitoring devices, and mobile health apps enable patients to access care from the comfort of their homes, improving convenience and adherence to treatment regimens.
Collaborative Innovation: Driving Progress Together
Collaboration between multidisciplinary teams of healthcare professionals, researchers, industry partners, and patient advocates is essential for driving innovation in renal care. By working together, stakeholders can leverage their collective expertise and resources to address unmet needs and accelerate progress toward better outcomes for patients with renal diseases.
The Future of Renal Care
As research continues to advance, the future of renal care holds promise for improved treatment options, enhanced patient experiences, and ultimately, better outcomes for individuals living with these complex conditions.
Advancements in Personalized Therapies
With the advent of precision medicine, the treatment landscape for renal diseases is expected to become increasingly personalized. Genetic testing and biomarker analysis will enable clinicians to tailor therapies to the specific needs of each patient, maximizing efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Innovations in Regenerative Therapies
Regenerative medicine is poised to revolutionize the treatment of renal diseases by offering the potential for tissue repair and regeneration. Emerging technologies such as bioengineered kidneys and organoids hold promise for providing patients with functional replacements for damaged tissue, reducing the need for lifelong dialysis or transplantation.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are being integrated into clinical practice to enhance diagnostic accuracy, predict disease progression, and optimize treatment strategies. AI-driven decision support systems can analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify patterns and trends that may not be apparent to human clinicians, leading to more personalized and effective care.
Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
The widespread adoption of telehealth and remote monitoring technologies will continue to expand access to renal care, particularly for patients in rural or underserved areas. Virtual consultations, remote monitoring of vital signs, and mobile health applications empower patients to actively participate in their own care while minimizing the need for in-person visits to healthcare facilities.
Patient-Centered Care Models
The shift towards patient-centered care models will prioritize holistic approaches that address not only the physical aspects of renal diseases but also the psychological, social, and financial impact on patients and their families. Integrated care teams composed of nephrologists, dietitians, social workers, and mental health professionals will collaborate to provide comprehensive support throughout the continuum of care.
Global Collaboration and Advocacy
Renal diseases represent a significant global health burden, necessitating coordinated efforts and advocacy initiatives on a global scale. International collaborations, research networks, and public health campaigns will play a crucial role in raising awareness, promoting early detection, and improving access to renal care services for all individuals, regardless of geographic location or socioeconomic status.
Conclusion
Renal diseases present significant challenges, but with proper management and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. By understanding the nature of these conditions, adopting healthy habits, and seeking assistance when needed, patients can navigate the journey from diagnosis to recovery with resilience and hope. The landscape of renal care is evolving rapidly, driven by ongoing research, technological innovations, and a growing emphasis on patient-centered approaches. With continued investment in research, collaboration, and advocacy, the future holds promise for better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals living with renal diseases.